Session 10: Analyzing Grammar
Important announcement about class schedule
Due dates
| Corpus Lab | Content | Due |
|---|---|---|
| Corpus Lab 1 | Basic Concordancing | Finished |
| Corpus Lab 2 | Lexical diversity, Lexical Sophistication | Finished |
| Corpus Lab 3 | Mini-search | 8/8 (Friday) |
| Corpus Lab 4 | Fine-grained syntactic complexity | 8/12 (Tuesday) |
The final submission of all the four Corpus lab is on 18th.
On Final Presentation
- You can choose your work from Lab 1, 3, or 4.
- 10 mins presentation
- Cover
- Research question
- Methods (corpus data, operationalization)
- Results
- Interpretation
On Corpus Lab 2
🎯 Learning Objectives
By the end of this session, students will be able to:
- Provide historical overview of the syntactic complexity research
- Describe different approaches to grammatical features:
- Syntactic complexity strand
- Fine-grained syntactic complexity strand
- Descriptive (register-based analysis) strand
- Verb Argument Construction (VAC) strand
- Understand current trends of syntactic complexity research
Warm-up question
Warm-up question
- When you learned Grammar in your second language, was it difficult?
- Which rule was easy for you to learn to use?
- Which rule was challenging for you to learn to use?
Overview
- Grammatical complexity strand
- Fine-grained grammatical feature strand
- Register-based / Multi-Dimensional Analysis strand
- Syntactic Sophistication strand
Syntactic complexity
In much SLA research, syntactic complexity has been used.
- Indicators of proficiency and development
Syntactic complexity strand
Syntactic complexity measures are categorized into:
- Type 1:
lengths of production - Type 2:
Sentence complexity - Type 3:
Subordination - Type 4:
Coordination - Type 5:
Particular structures
But before talking about each, we need to define units we use.
Unit Of Analysis
Unit of analysis is a terminology to indicate at which level you will conduct your analysis
- Lexical richness: word as unit of analysis
- Phraseological complexity: collocation, phrasal verb, etc.
- Syntactic complexity: Sentence, clause, etc.
Sentence
- A sentence (in English) is a unit starting with a capital letter and ends with a punctuation mark such as period, question mark, and exclamation mark.
T-unit
- Writing researchers often use Terminal-Unit (T-unit; Hunt, 1965) as unit of analysis.
- T-unit: An independent clause plus any dependent clauses attached to it
2 T-units: [The researcher loves vocabulary too much] [and he loves coffee too.]
1 T-units: [The researcher loves vocabulary and coffee too much because they have much in common.]How many T-units do the following example have?
- Because I was tired, I decided to take a break and watch a movie.
- I completed my assignment early, so I helped my friend review his draft, and we both felt more confident about our work.
Syntactic complexity measures - Length and Sentence
I completed my assignment early, so I helped my friend review his draft, and we both felt more confident about our work.
| Type | Measure | Code | Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lengths | Mean length of clause | MLC | (5+8+9) / 3 = 7.333 |
| Lengths | Mean length of sentence | MLS | 22 /1 = 22 |
| Lengths | Mean lengths of T-unit | MLT | (5+8+9) / 3 = 7.333 |
| Sentence | Clause per sentence | C/S | 3 / 1 = 3 |
Syntactic complexity measures - Clausal
Because I was tired, I decided to take a break and watch a movie.
| Type | Measure | Code | Score | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subordination | Clauses per T-unit | C/T | 2 / 1 = 2 | |
| Subordination | Complex T-units per T-unit | CT/T | 1/1 = 1 | |
| Subordination | Dependent clauses per clause | DC/C | 1/2 = 0.5 | |
| Subordination | Dependent clauses per T-unit | DC/T | 1/1 = 1 | |
| Coordination | Coordinate phrases per clause | CP/C | 1/2 = 0.5 | |
| Coordination | Coordinate phrases per T-unit | CP/T | 1/1 = 1 | |
| Coordination | T-units per sentence | T/S | 1/1 = 1 |
Syntactic complexity measures - Phrasal
Some complexity measures are at phrasal levels.
| Type | Measure | Code |
|---|---|---|
| Phrasal | Complex nominals per clause | CN/C |
| Phrasal | Complex nominals per T-unit | CN/T |
| Phrasal | Verb phrases per T-unit | VP/T |
- Complex nominals:
- nouns plus adjective, posessive, prepositional phrase, adjective clause, participle or appositive
- nominal clauses
- gerunds and infinitives in subject, but not object position
- Lu, X. (2011). A Corpus‐Based Evaluation of Syntactic Complexity Measures as Indices of College‐Level ESL Writers’ Language Development. TESOL Quarterly, 45(1), 36–62. https://doi.org/10.5054/tq.2011.240859
Organic approaches
- Norris & Ortega (2009) proposed an organic approach to look at the syntactic complexity.
- Critisized over-reliance on small number of measures (e.g., length-based measures)
- Move beyond whether or not complex; ask HOW.
- Researchers should select measures that reflect developmentally sensitive measures (Lambert & Kormos, 2014)
- Norris, J. M., & Ortega, L. (2009). Towards an Organic Approach to Investigating CAF in Instructed SLA: The Case of Complexity. Applied Linguistics, 30(4), 555–578. https://doi.org/10.1093/applin/amp044
- Lambert, C., & Kormos, J. (2014). Complexity, Accuracy, and Fluency in Task-based L2 Research: Toward More Developmentally Based Measures of Second Language Acquisition. Applied Linguistics, 35(5), 607–614. https://doi.org/10.1093/applin/amu047
Impact of situational variable on complexification
- Traditionally, researchers relied on Subordinate clauses .
- However, Biber showed that subordination is a characteristics of oral langauge.
- Instead, nominalization is one important feature of complexity in written language.
- Biber, D., Gray, B., & Poonpon, K. (2011). Should We Use Characteristics of Conversation to Measure Grammatical Complexity in L2 Writing Development? TESOL Quarterly, 45(1), 5–35. https://doi.org/10.5054/tq.2011.244483
Complexity features in Conversation vs academic writing
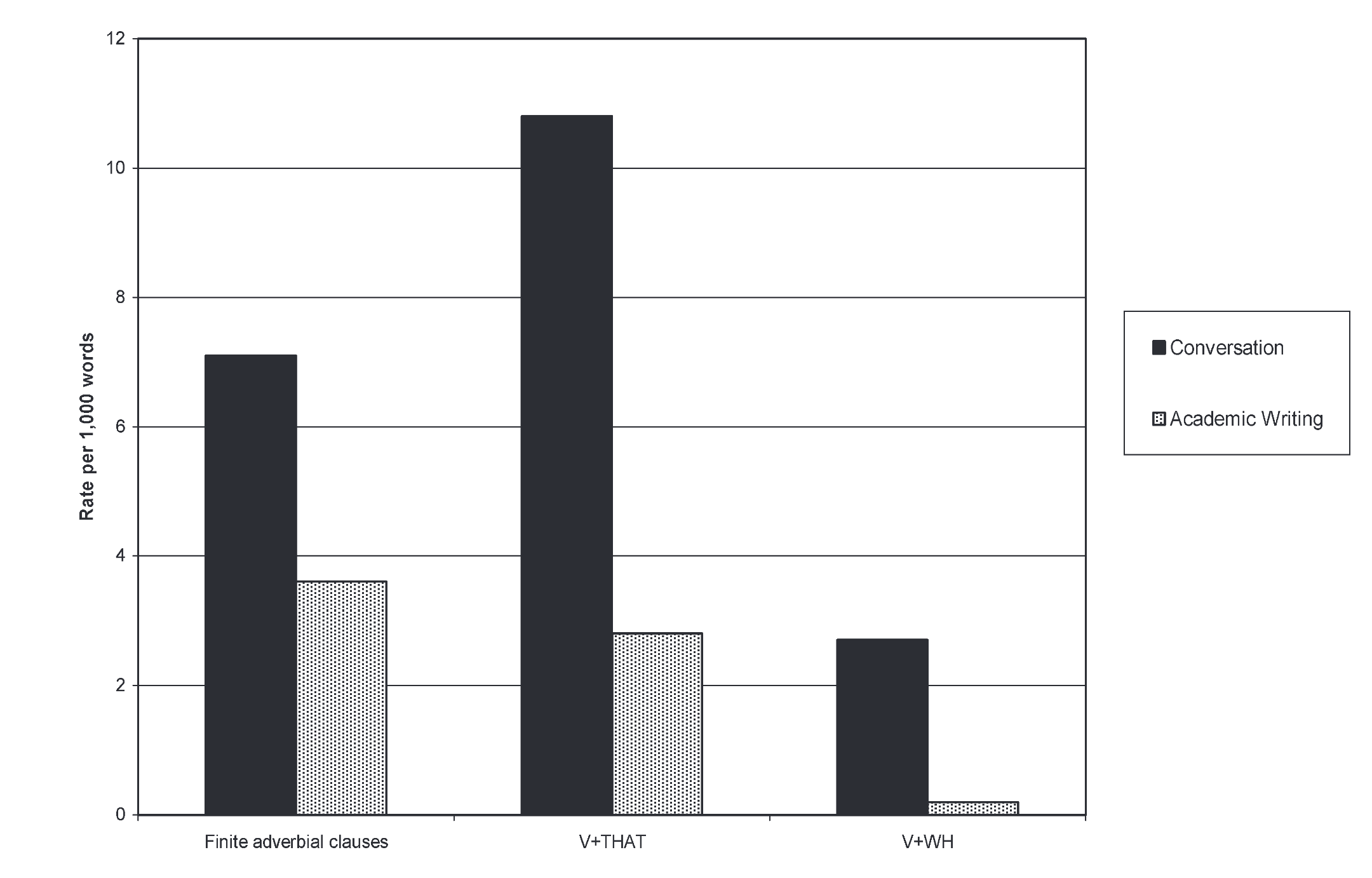
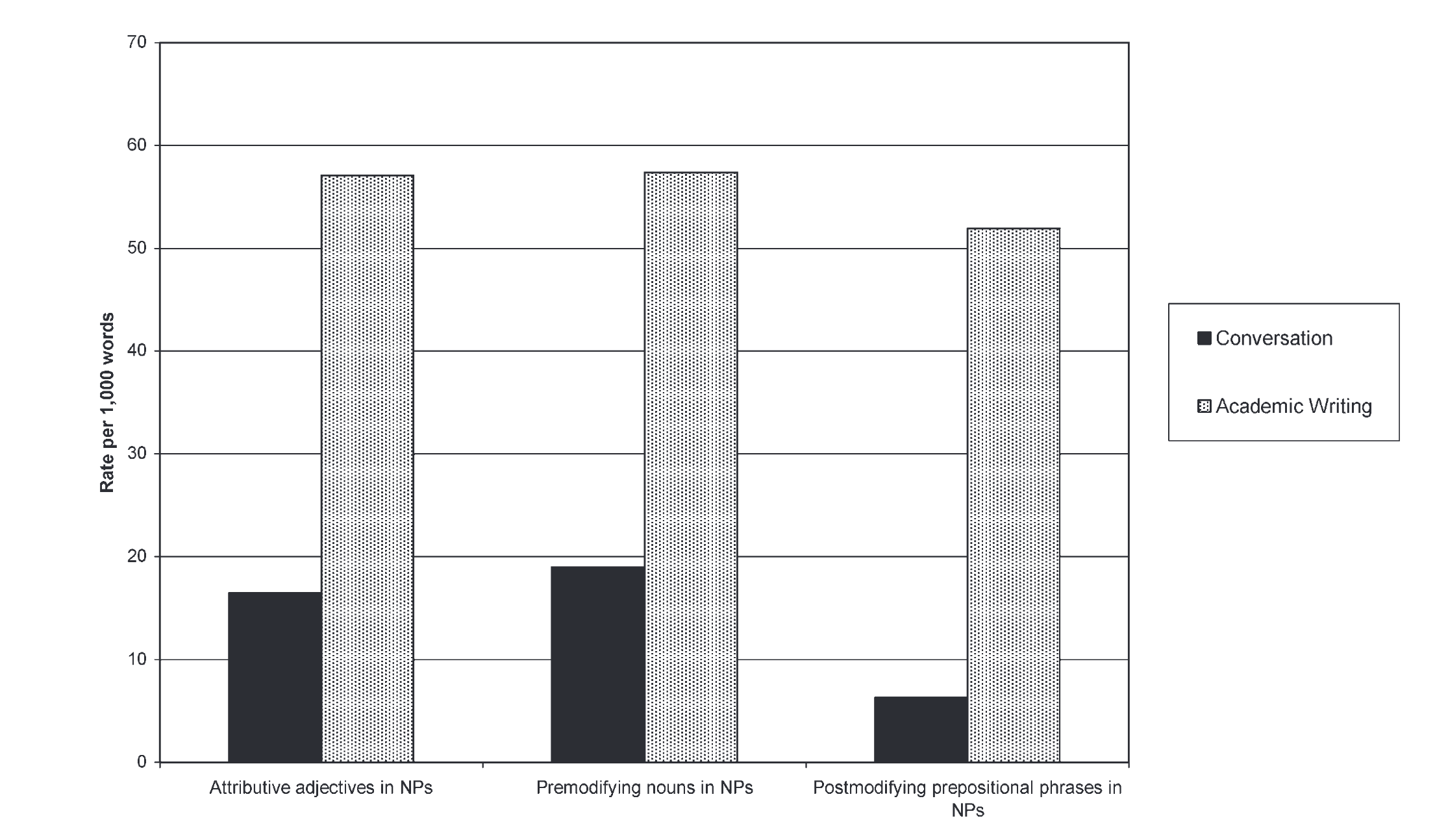
Complexity in conversation

Example from conversation
Complexity in academic paper
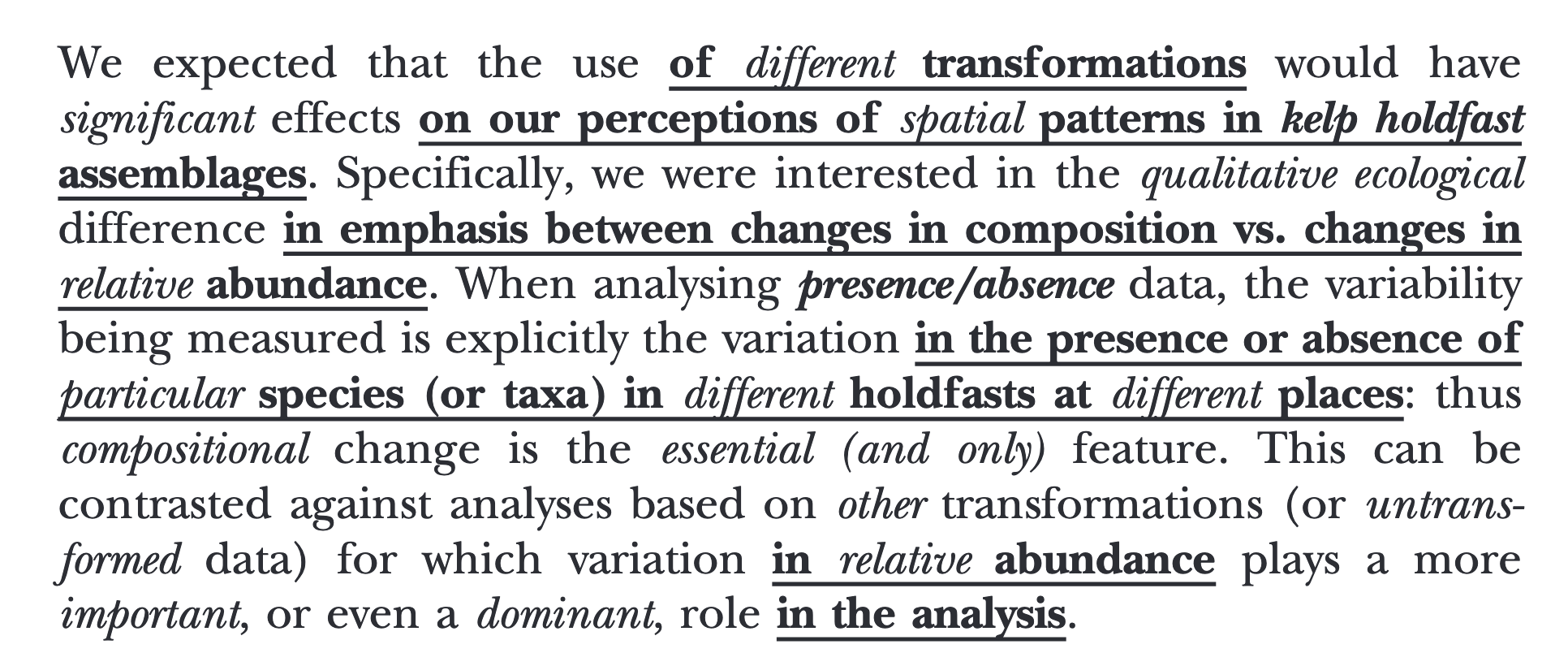
Example from academic paper
Discussion
- Any clarification questions?
- Have you thought of using any syntactic complexity measures in your study?
Fine-grained syntactic complexity strand
Fine-grained syntactic complexity strand
Criticism on the (largely) length-based grammatical complexity:
- Does not tell us about how sentence structures are elaborated
Length-based indices does not tell elaboration strategy
- The athletic man in the jersey kicked the ball over the fence.
- Elaborated by phrases (adjectival modification; prepositional phrases)
- Because he wanted to score a goal, the man kicked the ball.
- Elaborated by subordinate clause.
Example from Kyle & Crossley (2018)
Kyle & Crossley (2018)
- Kyle & Crossley (2018) proposed fine-grained clausal & phrasal complexity indices
- They used
dependencyparsing to identify fine-grained features of grammar.
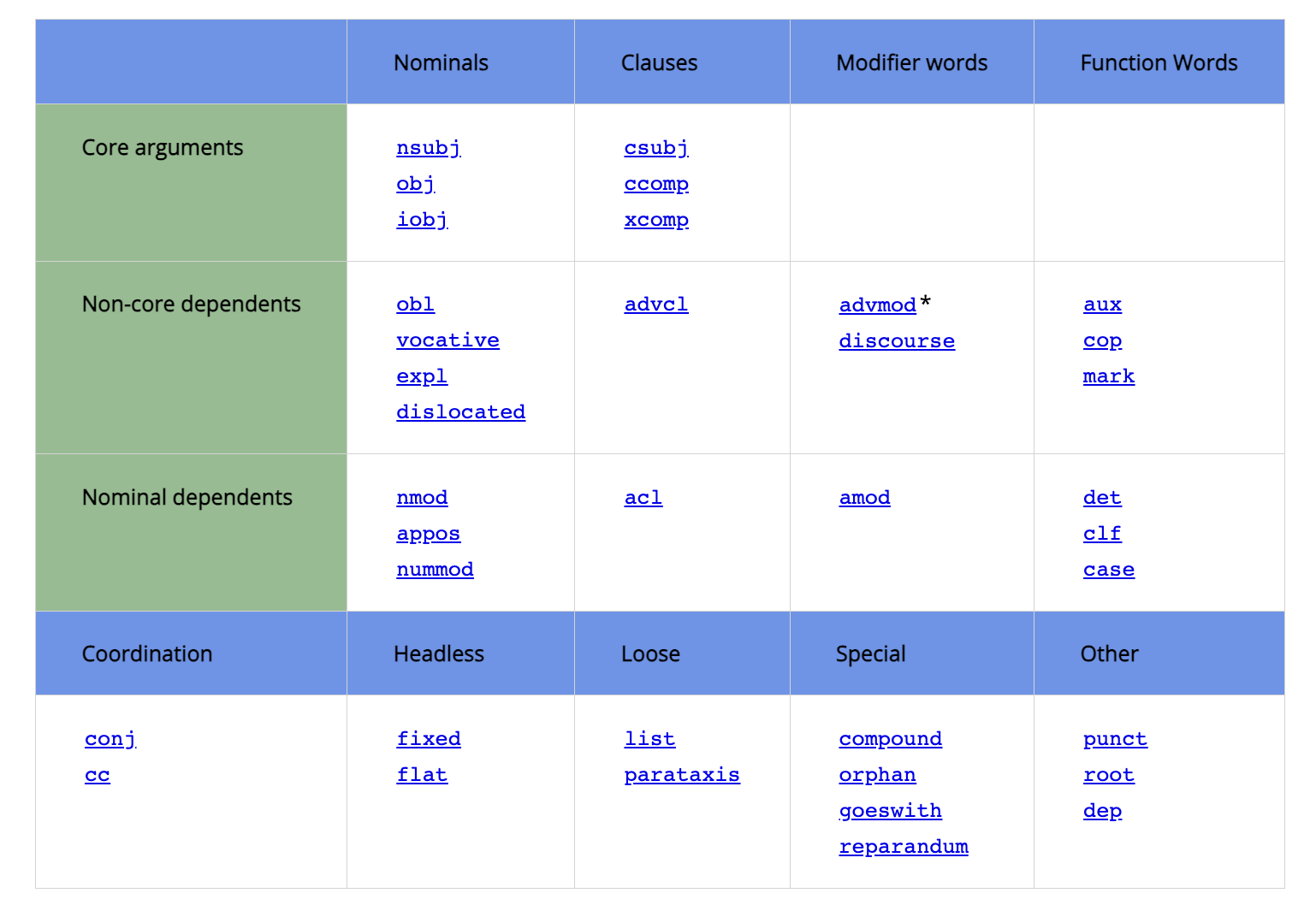
Dependency Parsing
Clausal indices
The followings are example:
| Structure | Dependency tag | Example of Structure |
|---|---|---|
| Nominal subject | nsubj |
The athlete ran quickly. |
| Direct object | dobj |
He plays soccer. |
| Indirect object | iobj |
He teaches me soccer. |
| Clausal complement | ccomp |
I am certain that he did it. |
| Adjectival complement | acomp |
He looks fine. |
| Nominal complement | ncomp |
She is a teacher. |
Clausal indices (Oblique)
The followings are example:
| Structure | Abbreviation | Example of Structure |
|---|---|---|
| Adverbial modifier | advmod |
Accordingly, I ate pizza. |
| Prepositional modifier | prep |
They went into the score. |
| Temporal modifier | tmod |
Last night, we had fun. |
| Adverbial clause | advcl |
The accident happened as night fell. |
| Open clausal complement | xcomp |
I am ready to leave. |
Phrasal indices
- Phrasal indices counts how many dependents there are for each of the following structure:
nsubj,nsubj_pass,agent,ncomp,dobj,iobj,pobj.
| Structure | Abbreviation | Example of Structure |
|---|---|---|
| Determiners | det |
The man went into the store. |
| Prepositional phrases | prep |
the man in the red hat. |
| Adjective modifier | amod |
The man in the red hat |
| Possessives | poss |
Tom’s store; his intention |
| Relative clause modifiers | recmod |
the plan I thought |
| Adverbial modifiers | advmod |
It’s a really good idea. |
Kyle & Crossley (2018)
- They counted fine-grained clausal and phrasal indices.
- # dependents per clause/phrase
- They examined correlations between TOEFL score and the fine-grained indices
Results
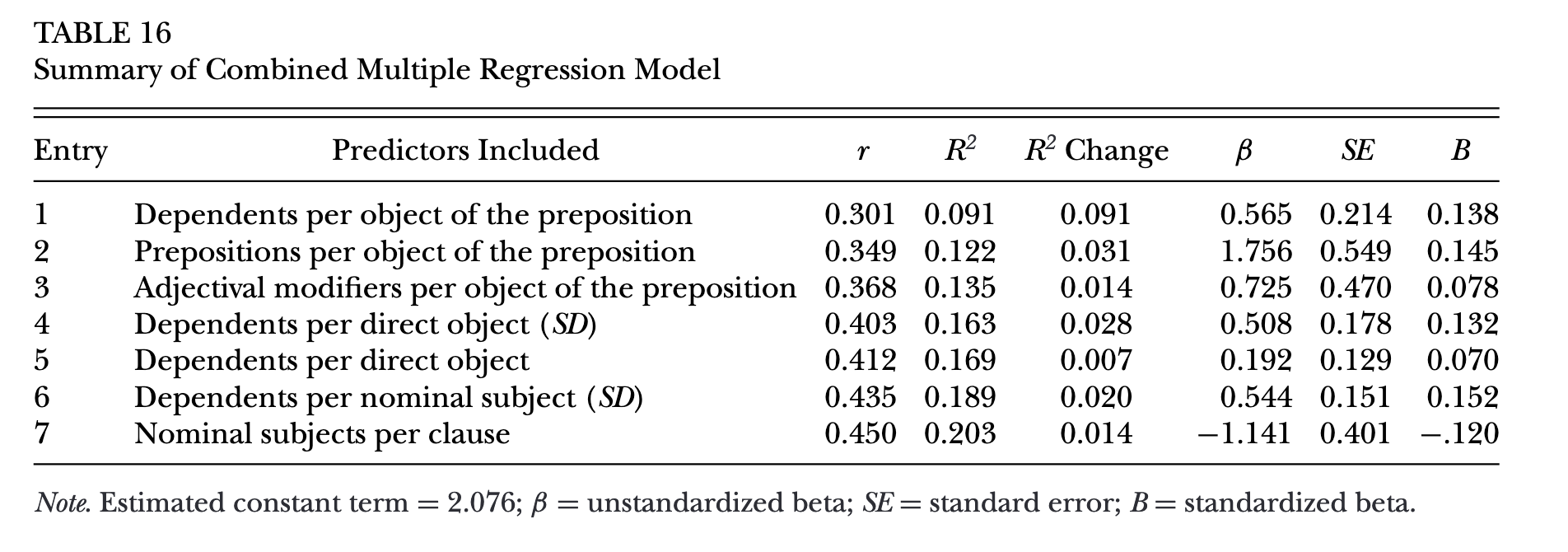
Final regression model
Example sentences
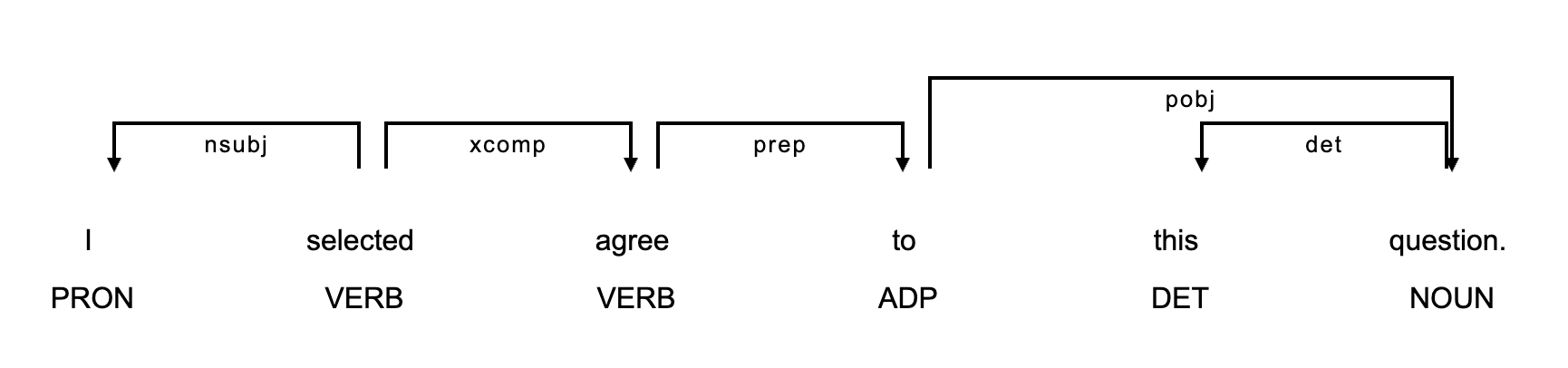
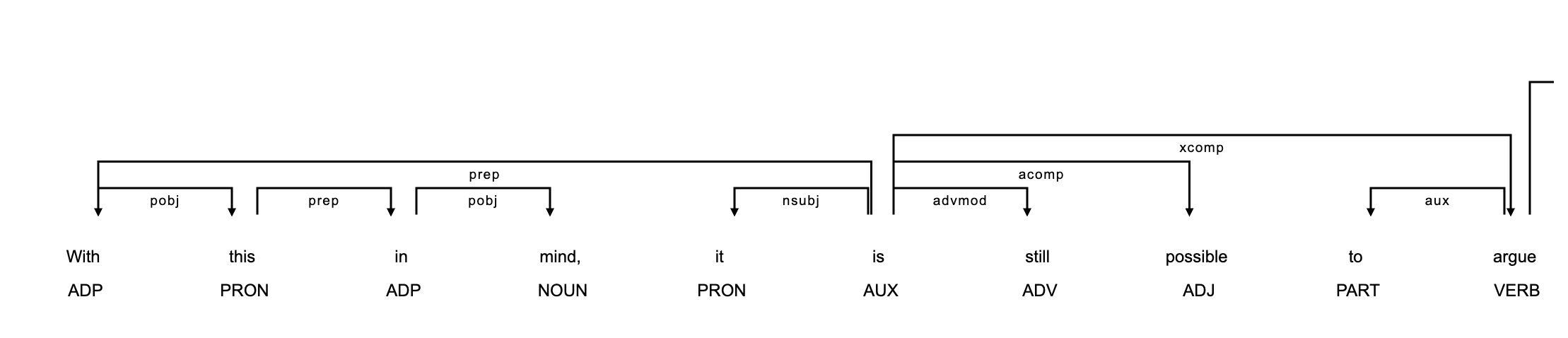
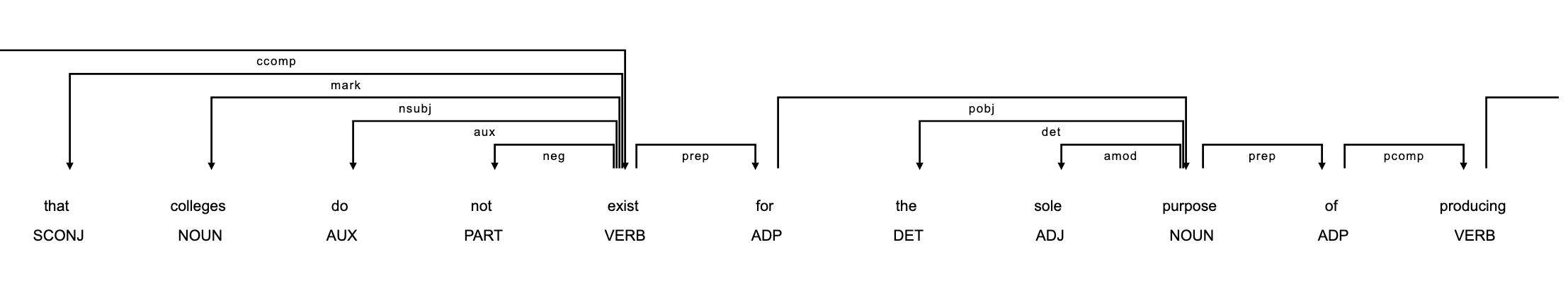
Kyle & Crossley (2018)
- The fine-grained indices:
- explained more variances (~ 20%) than traditional complexity measures (~ 5%)
- provides more insights into what structure the learners tend to use
- In hands-on activity, we will talk more about how to identify fine-grained grammatical features.
Register / Multi-Dimensional Analysis strand
Register / Multi-Dimensional Analysis strand
- This approach dates back to Biber (1988)
- He compared written and spoken language
- He developed Multidimensional Analysis
- Approach to characterize the grammatical features that distinguish registers using factor analysis.
Multidimensional analysis
- Prepare corpora from different textual genres (conversation, essay, recipe, etc.)
- Extract over 100 grammatical features (see next slide)
- Through factor analysis, examine how many groups of features (= dimension) can explain the linguistic variation in the corpus.
- Calculate dimension scores for each text
Examples of linguistic features
| Large Category | List of features |
|---|---|
| Pronouns and Proverbs | First person, Second person, Pronoun it, Proverb do |
| Reduced Forms | contractions, complementizer that-deletion |
| Prepositional phrases | All prepositional phrases |
| Nouns and noun types | Concrete noun, Cognitive noun, place noun, group noun, etc. |
| Verbs and verb types | tense aspect, modal verbs, mental verbs, causative verb, etc. |
| complement clauses | that complement, wh-complement |
| Nominal Postmodifying clauses | That relative clauses, wh-relative clauses |
Typical Result of MDA
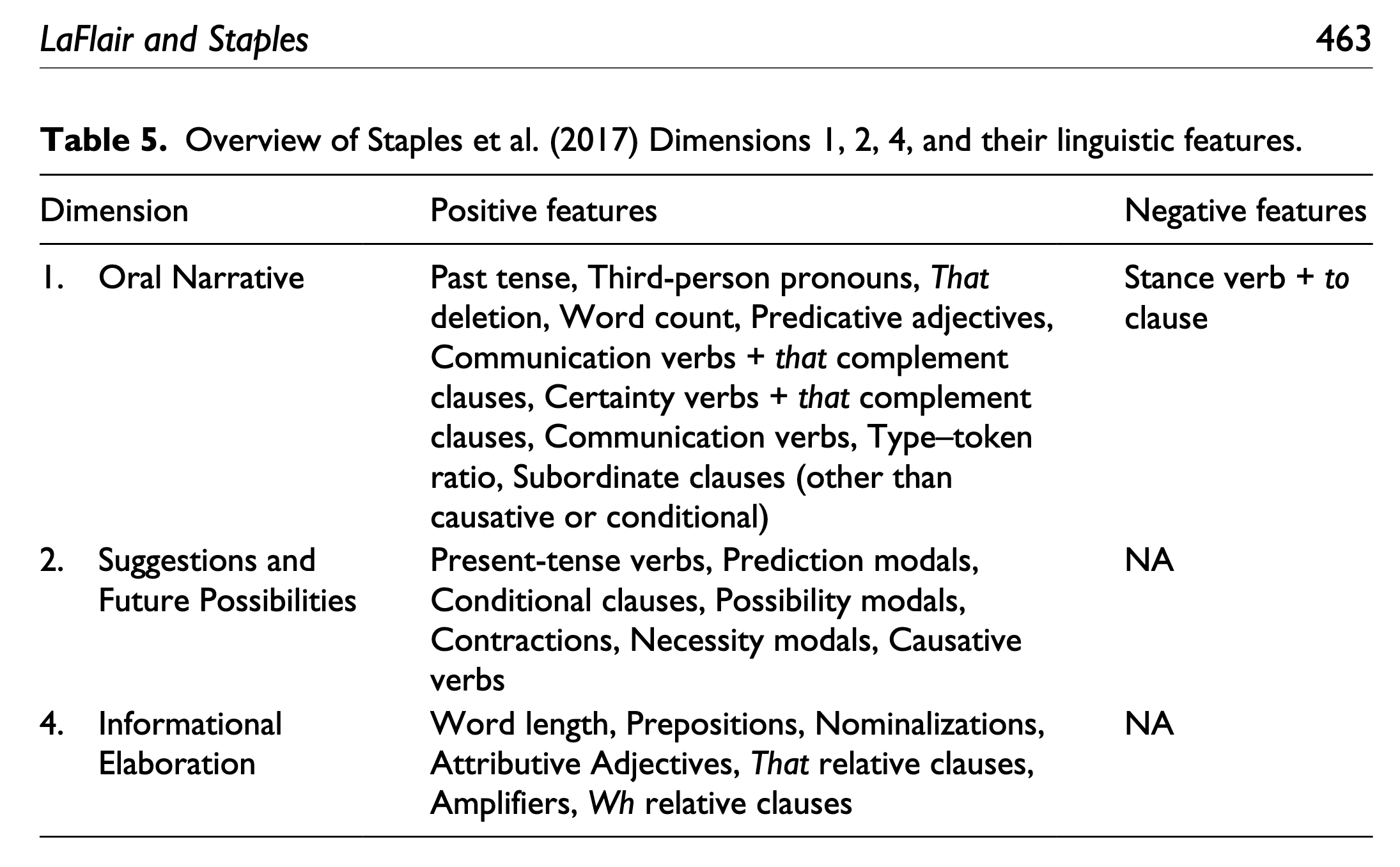
MDA
Dimension 4 Information elaboration
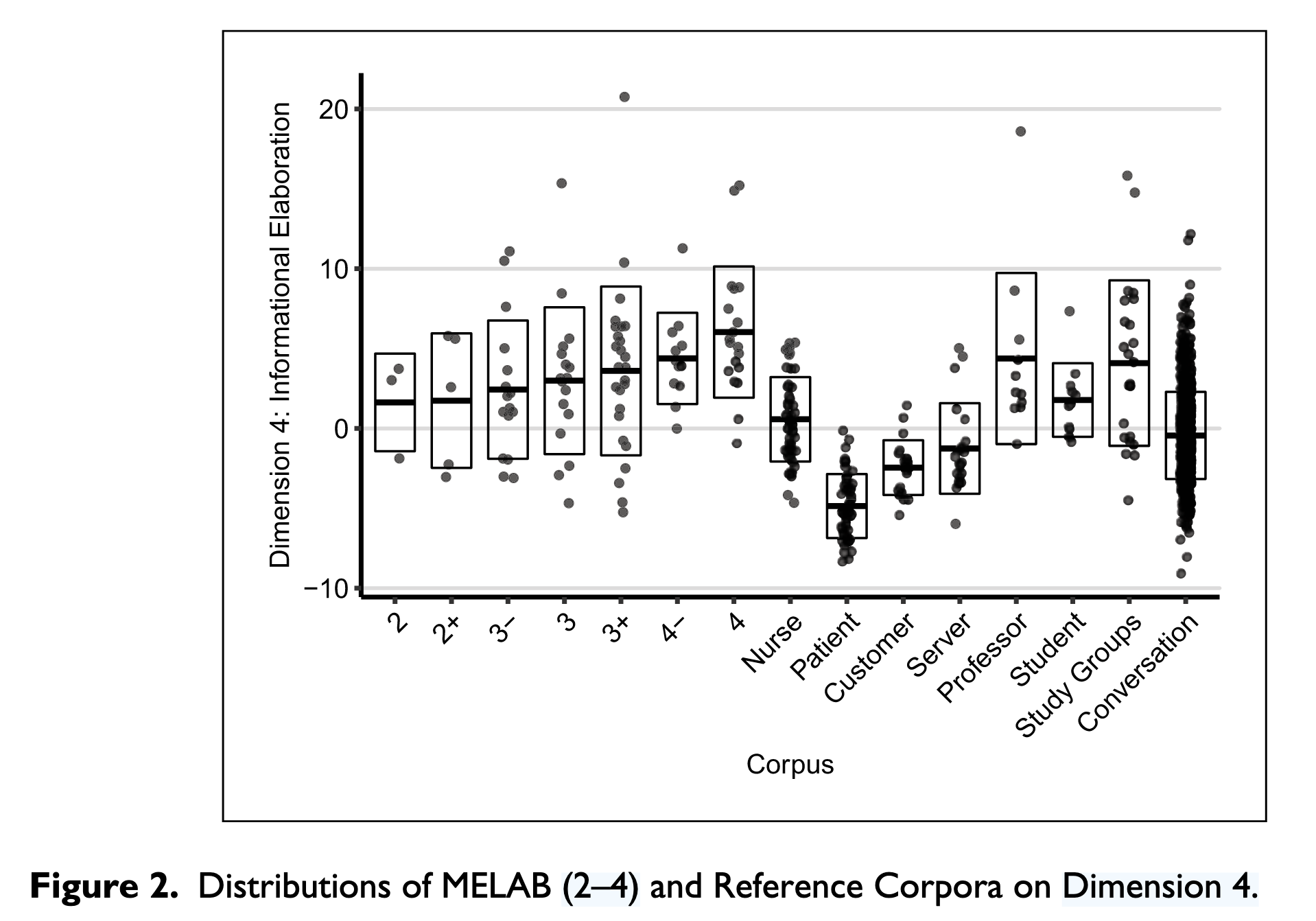
MDA - Dimension 4
High in information elaboration

discourse in text
Low in information elaboration

discourse in text
Syntactic sophistication strand
Syntactic sophistication (or VAC) strand
According to construction grammar (Goldberg, 1995, 2006), grammatical construction (structure) convey abstract linguistic meaning.
| Construction | Syntactic Frame | Semantic Frame | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| transitive | nsubj-root-dobj |
agent-V-theme | He loves coffee and skill acquisition theory. |
| ditransitive | nsubj-root-iobj-dobj |
agent-V-recipient-theme | I teach you NLP. |
| caused motion | nsubj-root-dobj-obl |
agent-V-theme-destination | Pat sneezed the foam off the cappuccino. |
| resultative | nsubj-root-dobj-xcomp |
agent-V-theme-result | She kissed him unconscious. |
- Goldberg, A. E. (2006). Constructions at work: The nature of generalization in language. Oxford University Press.
Approximating Verb Argument Construction (VAC)
- Kyle (2016) used “syntactic frame” based on dependency parsing to approximate VAC.
- He calculated frequency and SOA between
main verbandsyntactic frame.
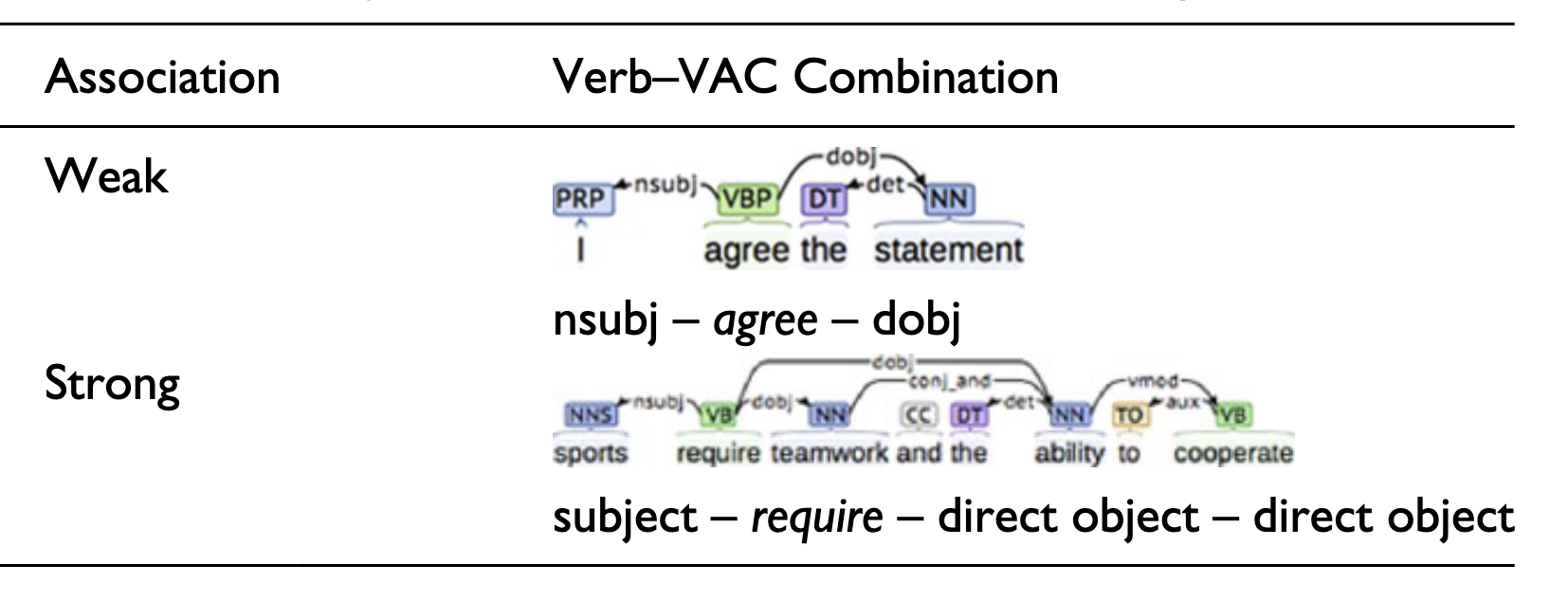
VAC example
Some VAC examples
| Main verb lemma | Verb Argument Construction | Example | Freq (PMW) in COCA |
|---|---|---|---|
| be | subject-verb-nominal complement | It is an indication of the ways… | 34,517.41 |
| say | subject – verb - clausal complement | He said [that health decisions should be made by patients and doctors] | 3865.16 |
| refuse | subject - verb - xcomp | He refused to brew a coffee to me. | 5540.0 |
| suppose | nsubj-v-ccomp | I suppose that the theory might be wrong. | 3016.0 |
Summary
We covered four different ways to look at grammar:
- Syntactic complexity
- Fine-grained syntactic complexity
- Register / MDA approach
- Syntactic sophistication
Linguistic Data Analysis I